Regeneration the regrowth of lost body parts normally follows – Regeneration: The Regrowth of Lost Body Parts Normally Follows is a fascinating phenomenon in biology that involves the ability of organisms to regrow lost or damaged tissues and organs. This process is essential for survival and adaptation in many species, and it holds great potential for medical and biotechnological applications.
Regeneration occurs through a complex interplay of cellular and molecular mechanisms, including stem cells, growth factors, and signaling pathways. The genetic regulation of regeneration is also crucial, and variations in regenerative capacities exist among different organisms and body parts.
Understanding Regeneration
Regeneration, the regrowth of lost body parts, is a fascinating phenomenon that has captivated scientists and researchers for centuries. It plays a crucial role in biology, enabling organisms to repair damaged tissues, maintain homeostasis, and even reproduce. There are different types of regeneration, including:
- Epimorphic regeneration:Regeneration of complex structures, such as limbs, from undifferentiated cells.
- Morphallactic regeneration:Regeneration of entire body parts from a fragment of the original.
- Compensatory regeneration:Regeneration of lost tissue to restore the function of an organ.
Mechanisms of Regeneration
Regeneration involves complex cellular and molecular processes. Stem cells, growth factors, and signaling pathways play critical roles in initiating and guiding the regeneration process.
- Stem cells:Undifferentiated cells that can give rise to multiple cell types, providing the building blocks for new tissues.
- Growth factors:Proteins that stimulate cell proliferation and differentiation, promoting the formation of new tissue.
- Signaling pathways:Networks of molecules that transmit information within and between cells, coordinating the regeneration process.
Genetic regulation also influences regeneration. Genes involved in cell cycle regulation, growth factor production, and signaling pathways have been identified as key factors in controlling regenerative abilities.
Examples of Regeneration

Many organisms exhibit remarkable regenerative abilities. Here are a few examples:
- Salamanders:Can regenerate entire limbs, tails, and even parts of their brains.
- Flatworms:Can regenerate their entire bodies from a small fragment.
- Starfish:Can regenerate lost arms, including the central disc.
Regenerative capacities vary among organisms. Some species can regenerate complex structures, while others are limited to regenerating simpler tissues.
Applications of Regeneration: Regeneration The Regrowth Of Lost Body Parts Normally Follows
Regeneration has potential applications in medicine and biotechnology. Tissue engineering and organ repair are promising areas where regeneration can be harnessed to treat diseases and injuries.
- Tissue engineering:Creating new tissues and organs for transplantation using stem cells and biomaterials.
- Organ repair:Repairing damaged organs by stimulating the body’s own regenerative processes.
However, challenges and ethical considerations need to be addressed before regenerative therapies can be widely used.
Regeneration in Different Body Parts
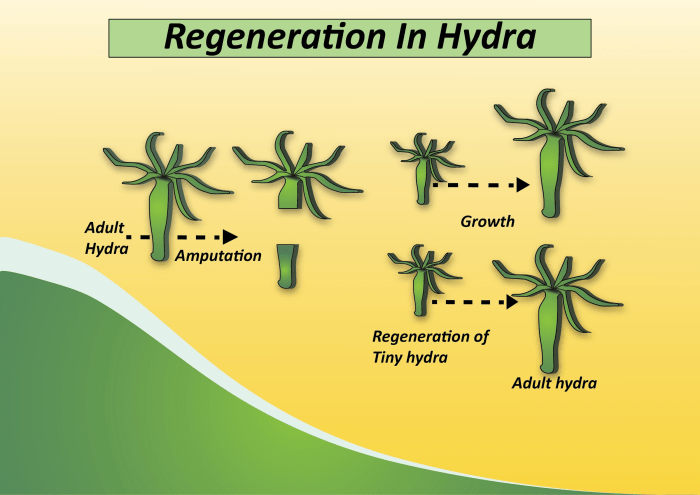
Different body parts have varying regenerative capacities. Limbs, skin, and internal organs exhibit different levels of regeneration.
- Limbs:Some organisms can regenerate complex limbs, while others have limited regenerative abilities.
- Skin:Skin has a high regenerative capacity, enabling it to repair wounds and maintain its integrity.
- Internal organs:Internal organs, such as the liver and kidneys, have limited regenerative capacities but can regenerate under certain conditions.
The regenerative potential of body parts is influenced by factors such as cell turnover rate, stem cell availability, and the presence of growth factors.
Regeneration and Evolution
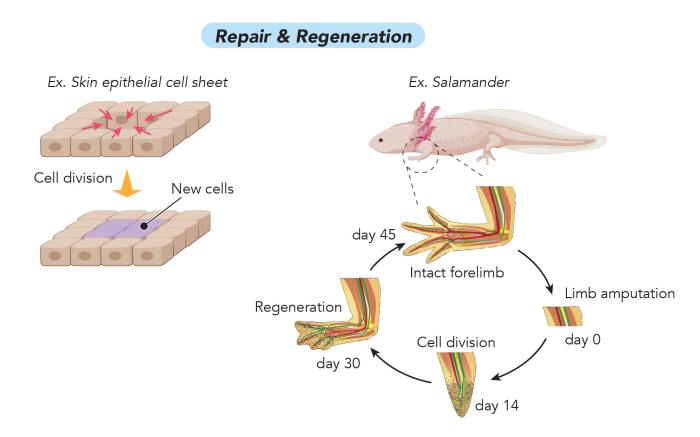
Regeneration has evolutionary significance, contributing to the survival and adaptation of species.
- Survival:Regeneration allows organisms to repair damaged tissues, increasing their chances of survival.
- Adaptation:Regeneration can enable organisms to adapt to changing environmental conditions, such as predator-prey interactions.
- Evolution:Regeneration has shaped the evolution of certain organisms, influencing their body plans and ecological niches.
Understanding regeneration can provide insights into evolutionary processes and the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
FAQ Guide
What is regeneration?
Regeneration is the ability of organisms to regrow lost or damaged tissues and organs.
What are the different types of regeneration?
There are three main types of regeneration: epimorphic, morphallactic, and compensatory.
What are the applications of regeneration in medicine?
Regeneration has potential applications in tissue engineering, organ repair, and regenerative therapies.